Are you new to WordPress and wondering, ‘What is WordPress Gutenberg?’ You are not alone! Many WordPress users familiar with the Classic Editor have the same question.
Gutenberg, also known as the WordPress Block Editor, was introduced in 2018 with the launch of WordPress version 5.0. It replaces the traditional WordPress Classic Editor with a more intuitive and user-friendly interface.
Yet, the question remains: What exactly is Gutenberg, and why is it important?
Don’t worry! In this Gutenberg editor WordPress tutorial post, we’ll answer the most pressing question, ‘What is WordPress Gutenberg?’ The pros and cons of the Gutenberg editor, how it works, and everything in between.
Ready? Let’s jump right in!
What is WordPress Gutenberg? – Brief Introduction
In WordPress, the Gutenberg editor, also referred to as the block editor, is the new way to publish content.
As we told you earlier, in December 2018, the Gutenberg editor was launched as the default editor in WordPress 5.0, replacing the classic editor.
The WordPress block editor has changed how we create web pages by introducing a block-based approach.
In Gutenberg, to create content layouts, you add a block for each element of the content. There are blocks for paragraphs, headings, images, galleries, videos, lists, and more.
It’s like building with Legos – each block represents a different element, from paragraphs and headings to images, videos, and widgets. Just like assembling a Lego house, you place blocks strategically to construct your web page, adding titles, content, and media as needed.
Still not quite sure, ‘What is WordPress Gutenberg?’ No worries—in this guide, we’ll describe everything about the WordPress Gutenberg editor and show you how to use the block editor for yourself. Let’s dive in!
Why WordPress Introduced Gutenberg Editor?
As of now, you better understand ‘What is WordPress Gutenberg?’ Before we show you how the WordPress block editor works, let’s find out why the WordPress team introduced the Gutenberg editor in the first place.
Over time, the Classic WordPress Editor, powered by TinyMCE, has remained largely unchanged, reflecting the typically slow and gradual pace of development within the WordPress core software.
However, the lack of evolution has made some elements, such as the Classic Editor, outdated (at least according to some users).
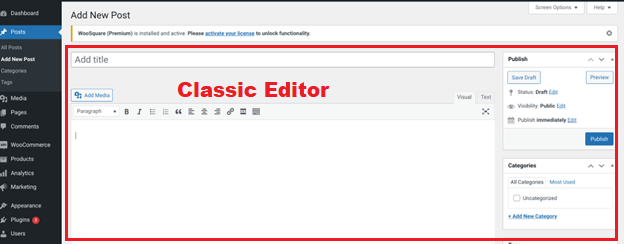
Over the past few years, online content creation has shifted towards a more visual and user-friendly approach. With the emergence of platforms like Wix and Squarespace, along with the popularity of drag-and-drop page builder plugins such as Elementor and Divi within the WordPress community, the demand for intuitive design tools has grown.
In response to this changing trend, WordPress introduced its own solution: Gutenberg.

So, the answer to your question of ‘What is WordPress Gutenberg?’ is that it’s a block-based editor that mirrors the functionality of popular page builder tools. It allows users to add customizable elements like images, paragraphs, lists, and buttons to their pages or posts as customizable blocks.
Next, we’ll discuss how the Gutenberg works. But first, let’s look into its potential pros and cons.
What are the benefits of Gutenberg WordPress?
If you’re currently using the Classic Editor, you might be considering a switch to Gutenberg. Likewise, if this is your first time using both editors, you’re probably curious about whether Gutenberg is the superior choice.
To make your decision easier, let’s explore the advantages and disadvantages of Gutenberg editor.!
Pros and Cons of WordPress Gutenberg Editor
Pros of Gutenberg Editor:
- Intuitive Content Creation: Gutenberg simplifies the content creation process, making it more beginner-friendly.
- Visual Representation: It provides a preview of your content that closely resembles how it will appear on the front end, which helps visualize the final layout.
- Unified Experience: By integrating various content elements, Gutenberg streamlines the content creation experience, eliminating the need for separate shortcodes.
- Customization Options: With a wide selection of elements at your disposal, Gutenberg offers extensive customization options.
- Native Integration: Gutenberg comes pre-installed with WordPress, so you don’t need to install additional plugins to use the page builder.
Cons of Gutenberg Editor:
- Steep Learning Curve: Although Gutenberg is quite easy to use, some users still find it difficult to learn all the options and settings, especially if they’re accustomed to the Classic Editor.
- Compatibility Issues: Transitioning from the Classic Editor to Gutenberg can cause issues with the site, which requires redesigning existing posts and pages.
In 2022, the WordPress team discontinued support for the Classic Editor. So, if you are still using the Classic Editor, it’s the perfect time to switch over to the WordPress Gutenberg Editor.
How to Access Gutenberg Editor in WordPress
Now that we’ve answered, ‘What is WordPress Gutenberg?” the pros and cons, it’s time for you to experience the Gutenberg Editor firsthand.
If you’ve freshly installed WordPress, Gutenberg comes pre-enabled and ready for you to use when you create new posts or pages.

Those who’ve updated their WordPress site to the latest version will find the option to edit your posts and pages with both editors.
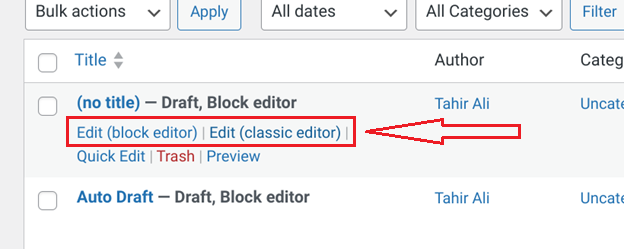
For those who are worried that opening your post in the Gutenberg Editor might break it, Consider testing Gutenberg on a local or staging site to resolve any issues without affecting your live content.
To get a better understanding of Gutenberg before installing it on your site, you can experiment with Gutenberg Editor on its official page.
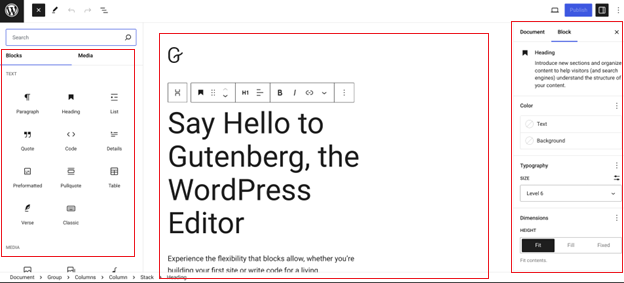
Here, you can explore different blocks, customize settings, and familiarize yourself with the editor’s features at your own pace.
How Does WordPress Gutenberg Editor Work?
In the Gutenberg editor, you create content using individual blocks. You can access these blocks via the plus icon at the top-left corner or directly within the page:
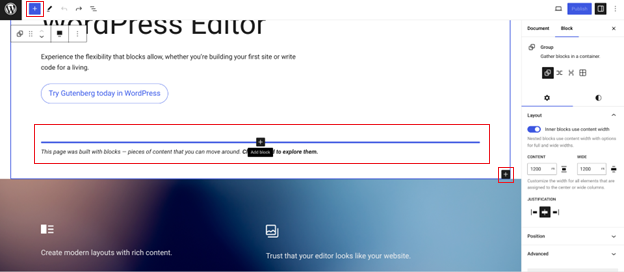
From paragraphs to images, lists, galleries, and tables, Gutenberg offers an array of blocks to suit your content needs.
For instance, a Paragraph block allows you to add text, create anchor links, adjust text color and typography, and more.
Once you select a block, you can customize each block further using the toolbar settings, and additional options are available in the right-hand sidebar.
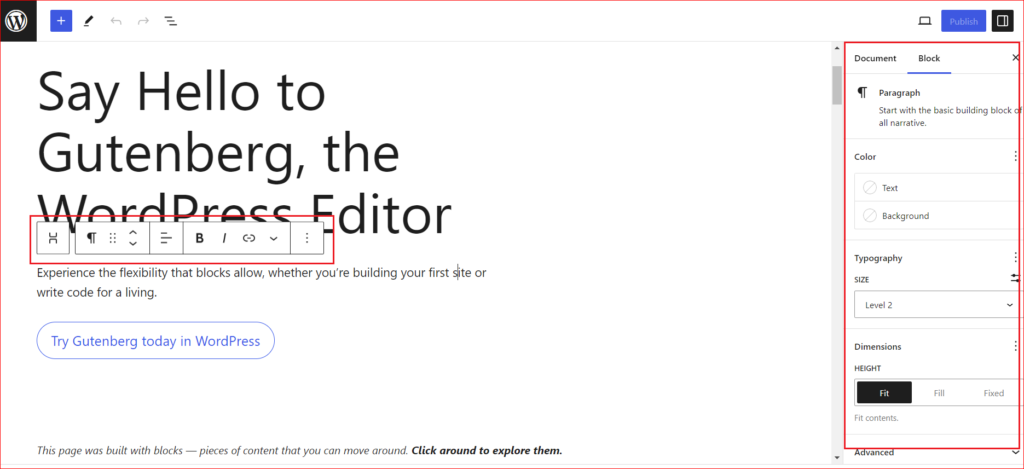
For example, if you’re working with a Paragraph block, you might create an anchor link, change the color and typography of the text, and more.
Simply put, Gutenberg simplifies content creation by allowing you to add and customize each element as a separate block and arrange them as necessary.
Moreover, Gutenberg includes pre-designed block patterns, offering ready-made designs for headers, galleries, and more.
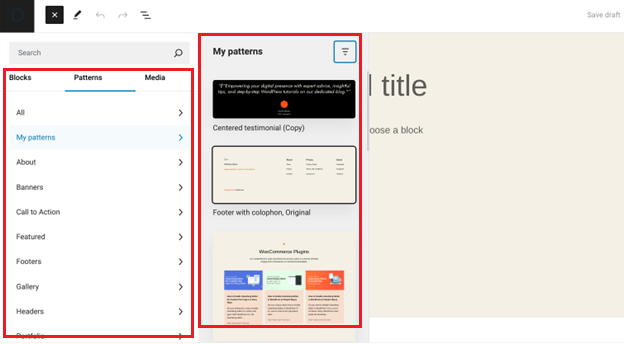
You can customize these patterns and save them as reusable blocks to integrate across different posts and pages.
Quick Tips and Tricks for Using WordPress Gutenberg Editor
The first step for creating eye-catching posts and pages with Gutenberg is to learn the basics. However, as you become more proficient with Gutenberg’s blocks over time, learning shortcuts and techniques can significantly enhance your workflow.
Next, learn how to use the keyboard shortcuts for Gutenben to make your workflow faster and easier.
Keyboard shortcuts for Gutenberg Editor
With Gutenberg keyboard shortcuts, you can work faster in the WordPress block editor. To access the list of shortcuts, click on the three-dot icon at the top-right corner of the editor. As shown in the screenshot below:

The following are some of the most useful keyboard shortcuts for Gutenberg:
NOTE: On macOS, replace Ctrl with Command ⌘ in the shortcuts.
| Action/Function | Keyboard Shortcut |
| To view keyboard shortcuts. | Shift+Alt+H |
| Global shortcuts | |
| Navigate to the nearest toolbar. | Alt+F10 |
| Open the command palette. | Ctrl+K |
| Switch between visual editor and code editor. | Ctrl+Shift+Alt+M |
| Toggle distraction free mode. | Ctrl+Shift+\ |
| Toggle fullscreen mode. | Ctrl+Shift+Alt+F |
| Show or hide the Settings sidebar. | Ctrl+Shift+, |
| Navigate to the next part of the editor. | Ctrl+` |
| Navigate to the previous part of the editor. | Ctrl+Shift+` Shift+Alt+P Ctrl+Shift+~ |
| Save your changes. | Ctrl+S |
| Undo your last changes. | Ctrl+Z |
| Redo your last undo. | Ctrl+Shift+Z Ctrl+Y |
| Open the block list view. | Shift+Alt+O |
| Selection shortcuts | |
| Select all text when typing. Press again to select all blocks. | Ctrl+A |
| Clear selection. | escape |
| Select text across multiple blocks. | Shift+Arrow |
| Block shortcuts | |
| Duplicate the selected block(s). | Ctrl+Shift+D |
| Remove the selected block(s). | Shift+Alt+Z |
| Insert a new block before the selected block(s). | Ctrl+Alt+T |
| Insert a new block after the selected block(s). | Ctrl+Alt+Y |
| Delete selection. | Del or backspace |
| Move the selected block(s) up. | Ctrl+Shift+Alt+T |
| Move the selected block(s) down. | Ctrl+Shift+Alt+Y |
| Change the block type after adding a new paragraph. | / |
| Text formatting | |
| Make the selected text bold. | Ctrl+B |
| Make the selected text italic. | Ctrl+I |
| Convert the selected text into a link. | Ctrl+K |
| Remove a link. | Ctrl+Shift+K |
| Insert a link to a post or page. | [[ |
| Underline the selected text. | Ctrl+U |
| Striketh through the selected text. | Shift+Alt+D |
| Make the selected text inline code. | Shift+Alt+X |
| Convert the current heading to a paragraph. | Shift+Alt+0 |
| Convert the current paragraph or heading to a heading of levels 1 to 6. | Shift+Alt+1-6 |
Extend WordPress Gutenberg Editor Functionality with Plugins
Up to this point, we’ve discussed ‘What is WordPress Gutenberg?’, the core features of the WordPress block editor. However, much like the rest of your WordPress site, you can extend the functionality of the Gutenberg editor with plugins.
There are many ways that plugins can enhance the Gutenberg’s functionality, such as:
- Adding New Content Blocks: Gutenberg plugins allow you to add new blocks to expand your design options.
- Modifying the Editor Interface/Features: With plugins, you can customize the editor’s interface and features, such as enabling better Markdown support.
- Introducing New Templates/Block Patterns: Some plugins use the core block patterns system, while others offer their own template systems.
In addition to plugins that are specifically designed for Gutenberg, many other WordPress plugins integrate with the Gutenberg editor.
For instance, a contact form plugin might provide a dedicated block for embedding forms, making it easier for users to embed forms.
Once you’ve grasped the fundamentals of the WordPress block editor, it’s worth exploring these plugins to discover them that can improve your experience.
Here are some popular options:
- Gutentor
- Getwid
- Stackable
- CoBlocks
- GenerateBlocks
- Kadence Blocks
- Ultimate Blocks
- Genesis Blocks
- Ultimate Addons for Gutenberg
Final Remarks on What is WordPress Gutenberg?
Now that you have understood ‘What is WordPress Gutenberg?’, you know the answer is quite simpler than you might think.
Basically, Gutenberg is an easy-to-use WordPress block editor that allows you to create pages and posts using blocks.
Since Gutenberg has become the default editor for WordPress, and support for the Classic Editor is no longer available, now is the time for you to get familiar with Gutenberg’s features.
To get in-depth insights about Gutenberg blocks and other features to create stunning posts and pages, check out our guide on how to use Gutenberg editor in WordPress.
Lastly, if you have any further questions or need assistance, feel free to ask them in the comment section below. We would love to help you!
Frequently Asked Questions
Do I need to install Gutenberg in WordPress?
Gutenberg comes pre-installed with WordPress since version 5.0, so there’s no need to install it separately. If you are using the old version of WordPress, then simply upgrade to the latest version, or you can install the Gutenberg WordPress plugin.
Is Gutenberg WordPress free?
Yes, Gutenberg is free, and it is the default editor for WordPress version 5.0 or higher.
Is Gutenberg better than Elementor?
Whether Gutenberg is better than Elementor depends on what you want. Gutenberg is the default editor for WordPress, with all the basic features and tools to create content. On the other hand, Elementor offers more advanced features and design options, which you might prefer for more complex websites.
How do you use Gutenberg in WordPress?
To use Gutenberg, simply create or edit a post or page in your WordPress dashboard. Gutenberg will automatically be available for you to use. To learn more, check out our guide on how to use Gutenberg editor in WordPress.
Can I still use Classic Editor along with Gutenberg?
Yes, you can use the Classic Editor plugin alongside Gutenberg if you prefer the old editing experience. Here is our detailed guide to learn how to switch between WordPress Classic Editor and Gutenberg.

![What is WordPress Gutenberg? [Ultimate Guide - 2025] What is WordPress Gutenberg?](https://www.wpdisc.com/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/what-is-wordpress-gutenberg-1024x520.png)

![How to Have 2 Lines of Text in WordPress Header [5 Easy Ways] How to Have 2 Lines of Text in WordPress Header [5 Easy Ways]](https://www.wpdisc.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/how-to-have-2-lines-of-text-in-wordpress-header-1024x520.png)

![How to Clone My Website to a Second URL [9 Easy Steps] How to Clone My Website to a Second URL [9 Easy Steps]](https://www.wpdisc.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/01/how-to-clone-my-website-to-a-second-url-1024x520.png)
Leave a Reply